Understanding the Intricacies of VPN: How Does it Work?
In an era where digital communication and data transfer dominate our daily lives, ensuring the security and privacy of online activities has become paramount. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) have emerged as a powerful tool to address these concerns. This technology creates a secure, encrypted connection over the Internet, allowing users to access the web with enhanced privacy and security. To comprehend how VPNs work, it’s essential to delve into the intricacies of their operation.
- The Basics of VPN: A Secure Tunnel
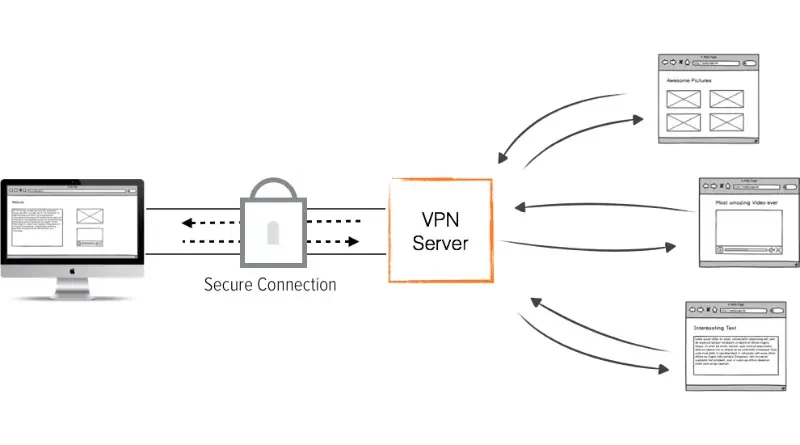
At its core, a VPN establishes a secure tunnel between the user’s device and the destination server, effectively encrypting the data transmitted between them. This encryption process converts the information into unreadable code, making it nearly impossible for unauthorized entities to decipher the content. This secure tunnel ensures that sensitive information, such as login credentials, personal details, and financial transactions, remains protected from potential threats.
- Encryption Protocols: Safeguarding Data Transmission
NordVPNs employ various encryption protocols to secure the data passing through the tunnel. Common protocols include OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, and IKEv2/IPsec. OpenVPN, known for its open-source nature and robust security features, is widely favored. These protocols use cryptographic keys to encode and decode data, ensuring that even if intercepted, the information remains indecipherable without the corresponding key.
- Authentication: Verifying User Identity
Authentication is a critical component of VPNs, ensuring that only authorized users gain access to the secure tunnel. Usernames, passwords, and security certificates are commonly used for authentication purposes. Some advanced VPNs also incorporate multi-factor authentication, adding an extra layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple means, such as a password and a unique code sent to their mobile device.
- VPN Server: The Gateway to Anonymity
A fundamental aspect of VPN functionality lies in its server infrastructure. When a user connects to a VPN, their internet traffic is routed through a remote server provided by the VPN service. This server, often located in a different geographical location, assigns the user a new IP address, masking their actual location and providing anonymity. As a result, users can access online content that may be restricted or geo-blocked in their region.
- Tunneling Protocols: Ensuring Secure Data Transmission
The process of encapsulating data within another data packet for secure transmission is known as tunneling. VPNs utilize tunneling protocols to create and maintain the secure connection. While OpenVPN is versatile and widely used, other protocols like PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) and L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) also contribute to the varied options available for users. Each protocol has its strengths and weaknesses, and the choice often depends on factors such as speed, security, and device compatibility.
- VPN and Public Wi-Fi: Shielding Against Cyber Threats
Public Wi-Fi networks, prevalent in cafes, airports, and hotels, pose significant security risks. Hackers often exploit these networks to intercept data transmitted by unsuspecting users. VPNs offer a crucial layer of defense in such scenarios by encrypting the data, thwarting any attempts to intercept sensitive information. This makes VPNs an invaluable tool for those who frequently connect to public Wi-Fi networks and need to ensure the security of their online activities.
- Bypassing Geo-restrictions: Unlocking Global Content
One of the primary advantages of VPNs is their ability to bypass geo-restrictions. Streaming services, websites, and online content are often limited to specific regions due to licensing agreements or government regulations. By connecting to a NordVPN server in a different location, users can circumvent these restrictions and access content as if they were physically present in the server’s location. This feature not only enhances online freedom but also enables users to explore a more open and diverse internet.
- VPN Logs: Balancing Privacy and Transparency
While VPNs are designed to prioritize user privacy, it’s essential to consider the logging policies of VPN service providers. Some VPNs keep minimal logs or adopt a strict no-logs policy, ensuring that user activities are not recorded. On the other hand, some providers may log certain data for troubleshooting or maintenance purposes. Users should carefully review a VPN provider’s privacy policy to understand the extent to which their data is retained and handled.
Conclusion: Navigating the Digital Landscape Safely
In a world where online privacy and security are paramount concerns, understanding how VPNs work is crucial for users seeking to safeguard their digital activities. By establishing secure tunnels, employing robust encryption protocols, and leveraging remote servers, VPNs create a shield against potential cyber threats. Whether it’s bypassing geo-restrictions, ensuring secure data transmission on public Wi-Fi, or enhancing overall online privacy, VPNs play a pivotal role in navigating the digital landscape safely and securely.